
The two processes are far more similar than you can imagine, says Dasarathi GV.
The term 'software development' is much misunderstood and misused. In India it is generally equated with writing code. In reality it is much more. The process of software development, you'll be surprised to know, is the same as the process of developing a new type of sambar.
These slides show you how. You can go through them the hard way, mentally answering the questions you encounter, or the easy way, just reading through them.
The choice is yours.

Step 1
You have a restaurant on this street. You think people are getting bored with the sambar that you have been serving and going to competitors. You want to invent a new type of sambar.
What is your first step?
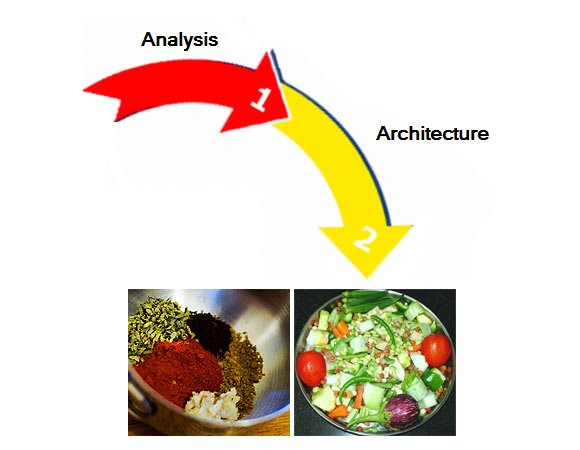
What is your next step, after analysing the need?
Architecture

What is your next step, after deciding the architecture?
Design

What is your next step, after deciding the design?
Coding
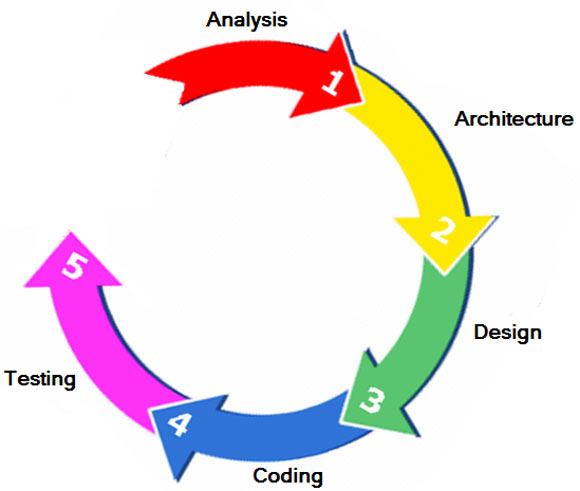
What is your next step, after making the sambar?
Testing
Check the taste, viscosity, temperature, aesthetics

What is the next step, after testing the sambar?
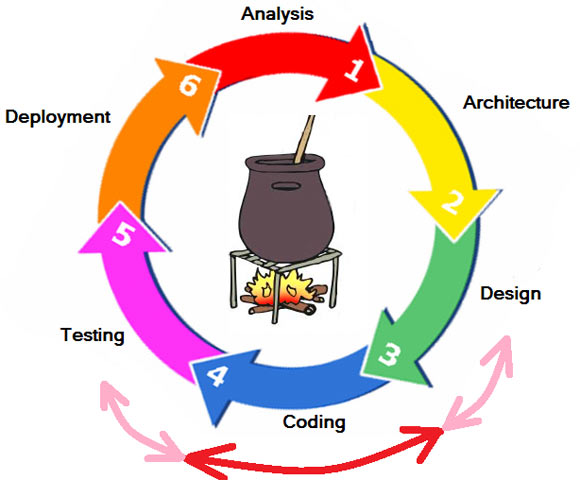
Deployment

'Know what' and 'Know how'
Steps 1 and 2 are the 'Know what'. What is required, what does the user want? This is called Domain knowledge.
Steps 3 to 6 are the 'Know how'. How can this requirement be fulfilled?
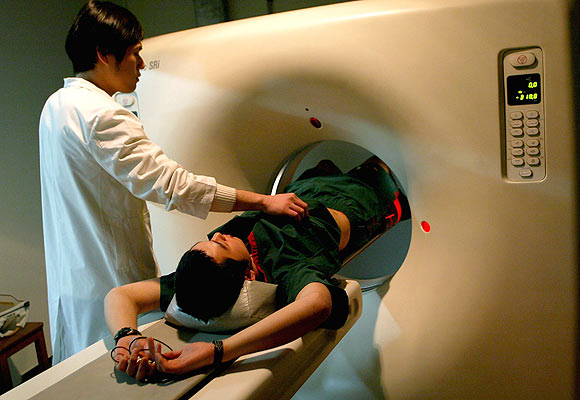
Example: Software for CT scan machine
The domain here is the human body.
Steps 1 and 2 can only be done by someone with domain knowledge of the human body -- a doctor.
Design, testing and deployment are jointly done by electronics, electrical and mechanical engineers.
Coding is done by a programmer.
Testing is done by a doctor.

Example: Aircraft head up display
The domain here is an aircraft. Steps 1 and 2 can only be done by someone with domain knowledge of flying an aircraft, a pilot. Design, testing and
deployment are jointly done by electronics, electrical and mechanical engineers.
Coding is done by a programmer.
Testing is done by a pilot.
'Software exports' from India
The reality
What is done is:

Skills required in software development:
6. Knowledge of user, user's requirements
5. Knowledge of application area, initial design
4. Writing software code -- Java, C++.
3. Knowledge of software design, mathematics
2. Knowledge of application area
1. Knowledge of user's requirements

Rewards in 'know what' and 'know how'
Know what:

Know how
The fat salary is immediate, because of the wage differential between India and the West. The salary curve will however flatten out fast, and you'll burn out fast without creative satisfaction.

Choose your software career wisely
Option 1
Join an IT services company as a programmer. Use your knowledge of programming languages like Java or C++ to do the coding for software.
Every six months or a year, keep shifting to a new software project -- banking, shoe retailing, airline ticket booking, finance. You will be a 'know how' person all your life, in step 3 in the circle, maybe graduating to step 4. You will have no domain knowledge in any particular domain.
Option 2
Join a software product company as a programmer. If you change jobs, stick to the same domain (example: banking) so your domain knowledge improves
as you put in more years on the job. You can move up to any of the steps, even 1 or 2.
Oh, by the way...
The 'sambar circle' applies to the development of any product, not just sambar or software.