Photographs: B Mathur/Reuters BS Reporter in Mumbai
Global risk aversion and India's widening current account deficit have dragged the rupee close to all-time low levels against the dollar.
Any fresh trigger from the troubled euro zone may push the Indian currency to the level of 52 against the dollar, say forex traders and economists.
Click on NEXT for more...
Falling rupee may breach 52 level against US$
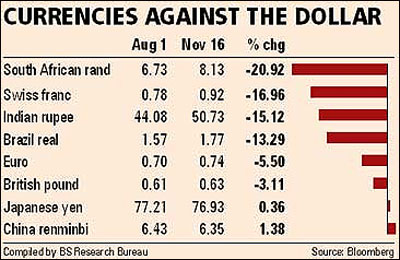
The rupee on Wednesday fell by seven paise to close at 50.73 against the dollar, inching closer to the all-time low of 51.97 seen in March 2009.
The Indian currency has lost around 15 per cent against the dollar in the past three months.
Click on NEXT for more...
Falling rupee may breach 52 level against US$
Image: US dollar notes are seen in a bank in Budapest.Photographs: Bernadett Szabo/Reuters
Severe implications
A weak rupee is not necessarily good news for exporters as the currencies of competing countries have fallen more or less to the same degree as the rupee
Import-dependent sectors have to pay more for raw material. Costlier crude means higher fuel prices, translating into further inflation
Gold and silver prices rise when the rupee depreciates. The benefits of an international price fall, if any, do not accrue to Indian importers
The Chinese currency is up 1.38 per cent while the rupee is down 15.12 per cent against the dollar since August. So, the Chinese can dump goods in Indian markets, taking advantage of the currency equation.
Click on NEXT for more...
Falling rupee may breach 52 level against US$
Photographs: Reuters
Traders said the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) intervened in the foreign exchange market to contain volatility.
The central bank was seen active in the three-month and six-month forward segment when the rupee was trading around 50.95.
After that, the rupee cooled off towards the end of the day's trade. RBI deputy governor Subir Gokarn had said it did not target any specific exchange rate but would intervene only to curb excess volatility.
"India's deteriorating current account balance is working negatively on the rupee. Exports are showing moderation while imports remain robust, leading to an outflow of dollars," says Madan Sabnavis, chief economist at rating agency CARE.
Given the adverse outlook on international trade and persistence of the debt crisis in Europe, the rupee may remain weak and touch 52 a dollar by the end of 2011, he says.
Click on NEXT for more...
Falling rupee may breach 52 level against US$
Photographs: Reuters
Consistent demand from oil importers, amid a strengthening dollar and fund outflows, is adding to the rupee's woes.
According to the Bombay Stock Exchange, there were net foreign fund outflows of Rs 488 crore on Wednesday as domestic equity markets fell around 0.7 per cent on Wednesday.
Finance minister Pranab Mukherjee on Wednesday said the central bank was closely watching the situation and would intervene if necessary.
Data show the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) sold dollars in September, a month the rupee fell 6.25 per cent.
"An RBI intervention at these levels may not help in the absence of similar action by other central banks," says a forex dealer with a private bank.
Click on NEXT for more...
Falling rupee may breach 52 level against US$
Photographs: Reuters
While importers are stuck with dollar payments, exporters are still holding on in expectation of a better rate.
On Tuesday, Kaushik Basu, chief economic advisor to the ministry of finance, said any bad news from the euro zone was bound to affect India. He said rupee depreciation was adding to inflation pressures.
International oil prices are ruling high. A weakening rupee is adding to importers' costs, ultimately leading to higher prices for consumers.






article